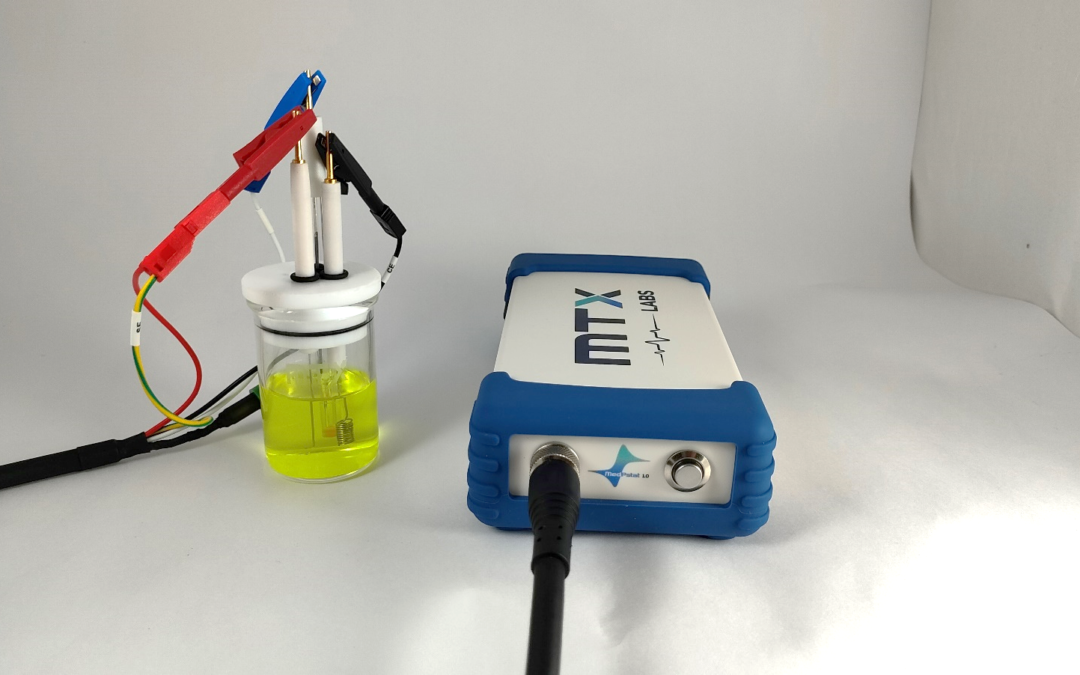
This application note provides a comprehensive manual for using the MedPstat device in Ferro/Ferri cyanide redox couple investigations. This Ferro/Ferri cyanide redox system is an excellent model for understanding cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical processes.
Introduction:
Cyclic voltammetry is a technique that provides valuable information about the electrochemical behavior of a material or a substance through redox reactions in the presence of systematically varied applied voltage/potential. The principle of cyclic voltammetry involves sweeping the voltage applied to an electrochemical cell back and forth between two limits while measuring the resulting electric current due to redox reactions happening at the surface of the working electrode. Cyclic Voltammetry provides information such as oxidation and reduction potentials, the number of electrons involved in the redox reactions, and the reaction kinetics.
Experimental:
Reagents:
Prepare a 50 mL stock solution in deionized water containing 5 mM K3Fe(CN)6 and 5 mM K4Fe(CN)6 in 1 M KCl.
Apparatus:
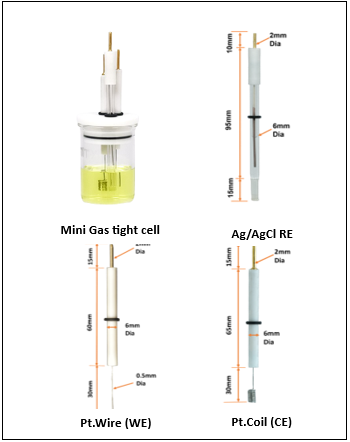
In this experimental arrangement, we employed the MedPstat, a portable and compact potentiostat that operates on the “MedEplot” software compatible with Windows. Notably, the software includes a Device status indicator, where Grey signifies no connection, Blue indicates readiness for connection, and Green denotes a connected device. For the electrochemical reaction, a 3-electrode voltammetry cell (MTX Labs mini gas-tight cell) was utilized, consisting of a Platinum Wire Electrode (MTX Labs, India) with an outer diameter of 6mm and an inner diameter of 3mm, a Silver/Silver Chloride Reference Electrode (MTX Labs, India) measuring and 6mm in diameter, and a Platinum Coil Counter Electrode with a length of 30mm. Before performing the experiment, rinse the electrodes with deionized water and gently wipe them with a tissue. The connection scheme between the potentiostat and the cells is identified by Red for the working electrode (WE), Blue for the reference electrode (RE), Black for the counter electrode (CE), and Red for Sensing (SE).
Procedure:
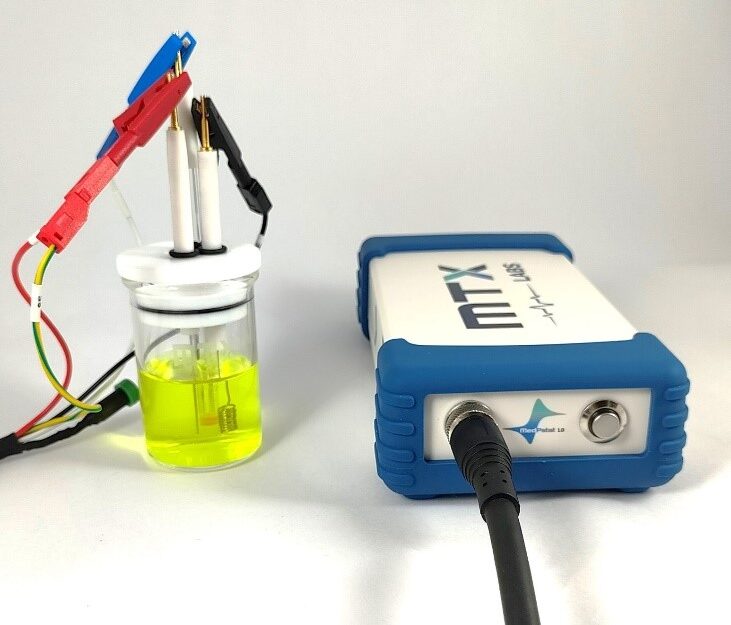
- Introduce 30ml of a 5mM Ferro/Ferri cyanide solution into the MTXC02 Mini gas-tight cell, ensuring there is sufficient volume for the electrodes to be immersed. Submerge the electrodes into the cell, and, if desired, insert an optional purging tube. Connect the electrodes following the previously provided instructions.
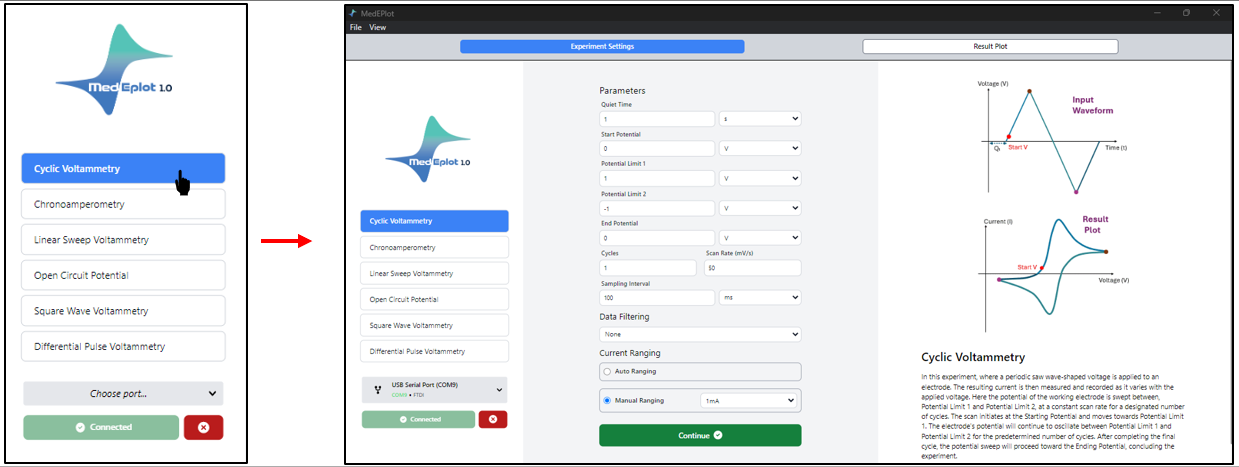
2. Press the Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) technique. Upon choosing cyclic voltammetry, the window divides into two sections. On one side, you’ve got the General Parameters box next to the experiment techniques, and on the other, you’ll find the fundamentals of cyclic voltammetry.
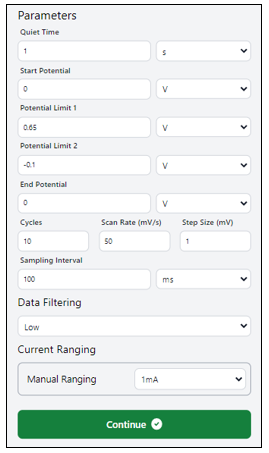
- simply click on the dialogue box to modify the values as needed. Follow the suggested settings or feel free to customize them, as demonstrated in the figure above. Press “Continue” to kick off the experiment. Once you do, a new window will pop up.
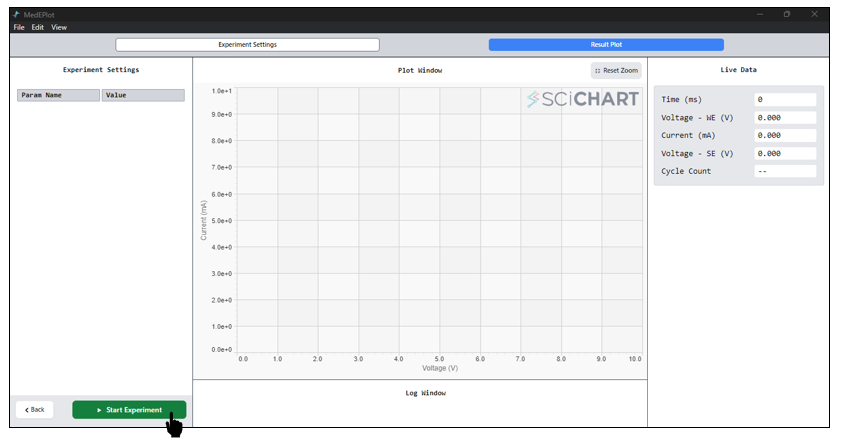
- you may initiate the experiment by clicking on “Start Experiment.”
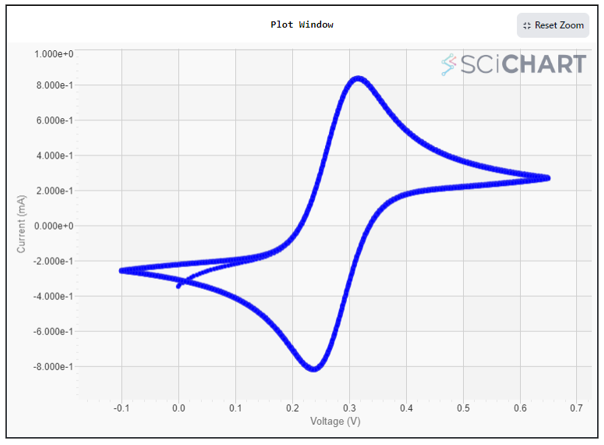
- The voltammogram will appear on the screen as it is produced. and it’ll adjust itself automatically when done. Here are the cyclic voltammetry results for 5mM Ferro/Ferri cyanide in 1M KCl. (Note: We’ve configured it for a total of 10 cycles.)
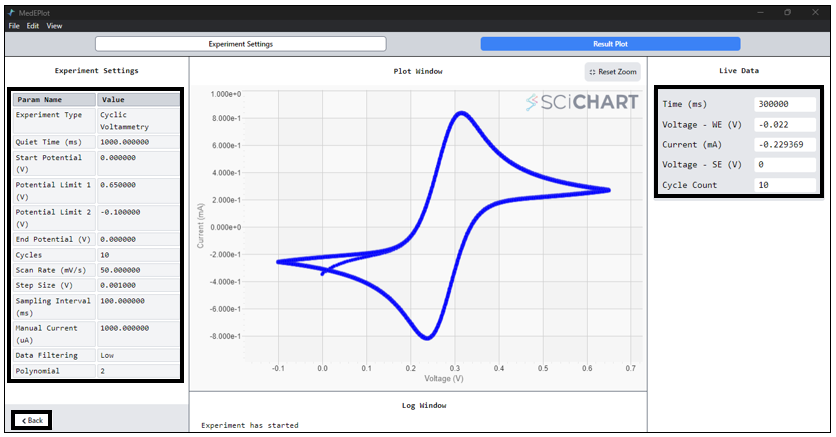
- In the Cyclic Voltammogram window, access experimental settings on the LEFT, observe real-time data on the RIGHT, and find the completion status at the bottom. To return to the main window or initiate another experiment, simply press the ‘BACK’ button.
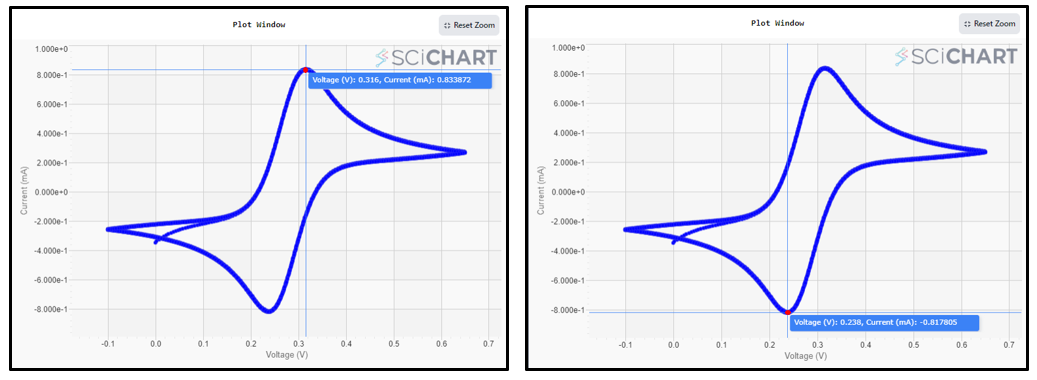
- After identifying both the anodic and cathodic peaks, simply click on the arrow symbol adjacent to the peak to access the numerical values associated with these peak parameters.
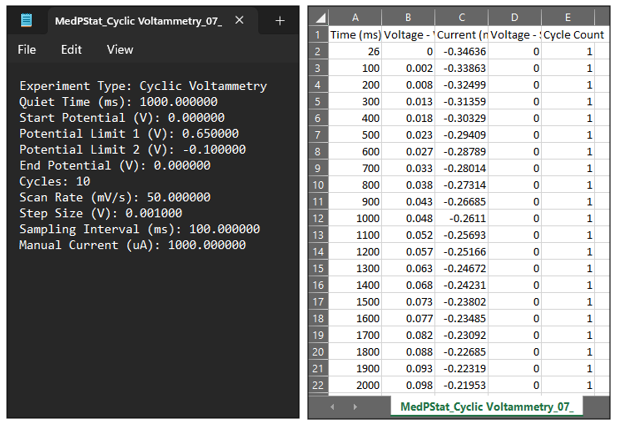
- Once the experiment is completed, navigate to the MedEplot software and access the data folder. Within this folder, you will encounter two sets of files: one comprising the experimental data file (.txt), and the other consisting of the Excel sheet data file (.csv).
Thanks for choosing MedPstat as your research companion.
MTX Labs Team

