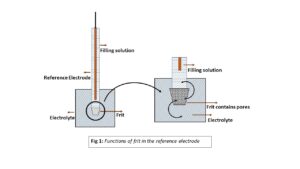
The porous frit at the tip of the reference electrode (RE) acts as a semi-permeable membrane facilitating ions exchange between RE’s filling solution (3M NaCl/KOH) and electrolyte while avoiding direct physical interaction between the two as shown in Fig 1. The primary function of the frit is to lower the leak rate and to determine the stability of the reference electrode (RE) while using a potentiostat. The reference electrode without frit tip will lead to electrolyte contamination.
For example, A junction potential arises at the interface of two ionic solutions due to differences in the compositions, concentrations, and mobility of the ions. The Positive and negative ion activity in each solution is different, and diffusion happens at the contact surface of both liquids, generating a difference in the RE potential. So, the liquid junction potential is increased which creates more fluctuations in the RE potential, frits assist in reducing the fluctuations.